
It will soon be five years since Amazon acquired Whole Foods Market and made its first foray into the brick and mortar grocery space. We dove into the data to understand Whole Foods’ evolution since the acquisition, see how the legacy grocery is recovering from the pandemic’s impact and determine what may be next for the Whole Foods-Amazon partnership.
Whole Foods’ Acquisition
In June 2017, Whole Foods Market and Amazon announced that Amazon would acquire Whole Foods. For Amazon, the acquisition presented an opportunity to learn the ins-and-outs of running a brick-and-mortar grocery business without setting up a costly physical infrastructure or going through the usual trial and error. By the time Amazon rolled out its Amazon Fresh stores, the online behemoth had accumulated wide ranging industry knowledge through its Whole Foods operations. Amazon could also use the insights gained from analyzing Whole Foods consumer data to improve its online grocery offerings. And beyond groceries, Amazon could use Whole Foods’ extensive store fleet to improve Amazon’s physical footprint.
The partnership seemed to be a natural match. While the sale of Whole Foods to Amazon signaled a turning point in the world of online groceries, the natural grocer was already experimenting with e-commerce and omnichannel before Amazon entered the picture. Whole Foods first announced the launch of a limited e-commerce platform in 1999 and partnered with instacart to offer delivery and in-store pick-up options back in 2014, when instacart was still a bona fide start-up. The Amazon deal empowered the grocer to take its technological capacities even further.
At the time of the acquisition, Whole Foods was being pressured by investors to sell or make significant changes to the business model. The brand credited with transforming the natural and organic grocery space from niche to mass market was seeing increased competition from other grocers who had begun carrying organic and natural products at lower prices, and this competition was eating away at Whole Foods’ profits. But even if Whole Foods had somewhat tapered off, the natural grocery was still growing – until the pandemic hit in March 2020.
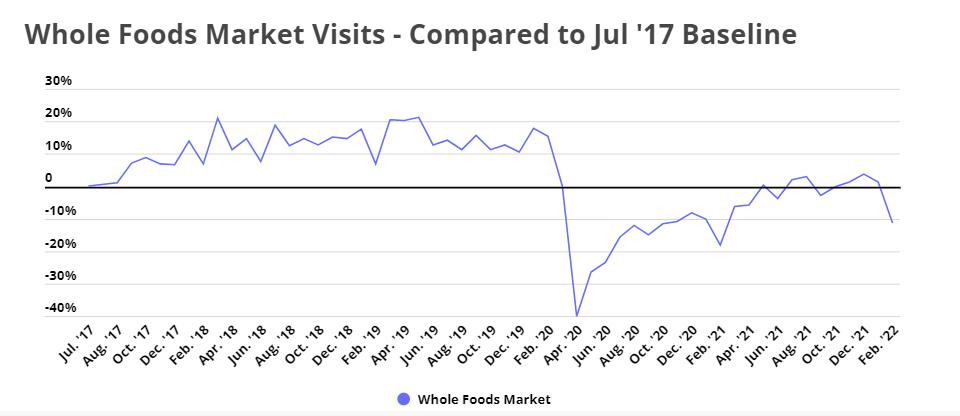
Difficult COVID Recovery – But Recovery Nonetheless
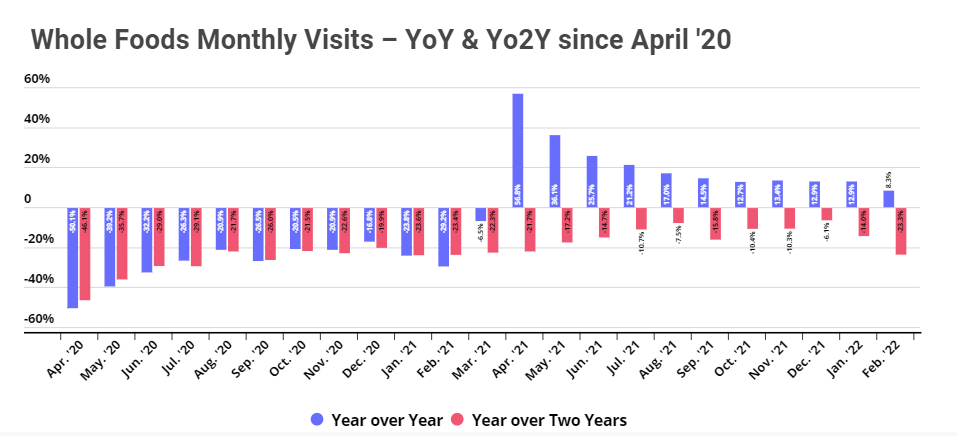
Visits to Whole Foods have not fully recovered from COVID’s impact, but are certainly on the rebound. A key element of this has been the brand’s orientation towards urban areas and a lesser orientation towards value shopping – two elements that have impacted visits in the current environment.
Another part of the continued foot traffic decrease could be due to shoppers purchasing Whole Foods products through other channels. Amazon had already incorporated Whole Foods into its e-commerce machinery in October 2019 when it launched free grocery delivery for select prime members. And the internet giant subsequently announced that grocery delivery orders from Amazon Fresh and Whole Foods Market more than doubled in Q4 2019 on a year-over-year basis. And in October 2020, when it became apparent that the pandemic was not letting up, Amazon launched free, one-hour grocery pickup at all US Whole Foods Market locations.
Beyond expanding customers’ digital access to Whole Foods, the partnership also created new opportunities for shoppers to visit Whole Foods locations, which may have boosted foot traffic during the pandemic-induced lull. In December ‘20, Amazon began offering customers the option of returning products purchased on Amazon.com to Whole Foods venues, with select stores now offering free “no-box” returns and return lockers to simplify the process even further. So far, however, these additional opportunities for physical visits have yet to translate into increased foot traffic, although the grocer has seen its YoY visits increase since the pandemic lows of 2020.
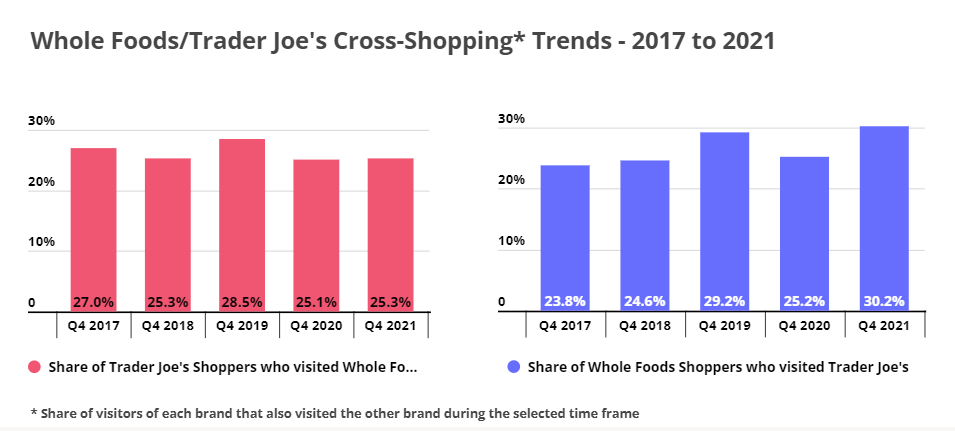
Understanding Whole Foods through the Lens of Trader Joe’s
Trader Joe’s seems like the natural counterpart to Whole Foods – another national chain that brands itself as a health-conscious grocer that carries a variety of organic and natural foods. Unlike Whole Foods, however, Trader Joe’s is not publicly traded (nor is it owned by a publicly traded company). More importantly, Trader Joe’s does not operate its own e-commerce channel, emphasizing the in-store experience instead. While Trader Joe’s also suffered a pandemic-induced setback in visits, the California-based brand had returned to YoY visit growth by July 2020.
Comparing cross-shopping trends for the two brands – as measured by the number of one chain’s customers who also visited the other chain during a given timeframe – shows that Trader Joe’s seems to be slowly gaining on Whole Foods. In Q4 2017 – the first full quarter of Amazon’s Whole Foods ownership – 27.0% of Trader Joe’s customers visited a Whole Foods, while only 23.8% of Whole Foods customers visited a Trader Joe’s. By Q4 2021, only 25.3% of Trader Joe’s customers were cross-shopping at Whole Foods, whereas cross-shopping from Whole Foods to Trader Joe’s had grown to include 30.2% Whole Foods customers. Much of this centers arounds the continued challenges that Whole Foods has faced on a nationwide level, but also indicates that one potential beneficiary of those struggles could be Trade Joe’s.
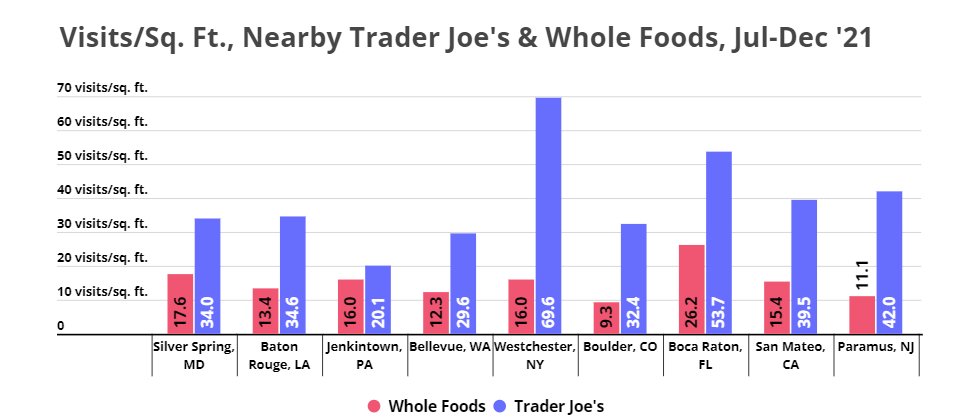
Customers Value Experience
In a survey we conducted in March 2022 of U.S. based adults aged 18 to 64, 29.4% of respondents stated that the in-store experience affected their choice of which grocery store to visit. For 18 to 24-year-old respondents, that share climbed to 44.4%. At the same time, only 38.3% of respondents (and 30.2% of 18 to 24-year-old respondents) stated that they were visiting grocery stores less frequently now than they had been pre-pandemic. This means that no matter how sophisticated a grocer’s online ordering, delivery, and pick-up mechanism is, most customers – including in key demographic segments – still want to visit physical grocery stores and have a positive shopping experience in the store.
Comparing visits per square foot for nine Trader Joe’s/Whole Foods stores that are less than three miles apart from each other shows how much more crowded the Trader Joe’s tend to be. Part of the reason for the significantly higher visits-per-sq. ft. to Trader Joe’s stores is that Trader Joe’s stores are typically much smaller than Whole Foods stores. But another major reason is that Trader Joe’s has found a way to make shopping in its stores seem exciting, with the promise of being able to get certain products that are just not available elsewhere; customers are willing to brave the crowds in exchange for getting a taste of the unique Trader Joe’s experience.
Amazon knew that the shopping experience was critical when it purchased Whole Foods in 2017. As Jeff Bezos, Amazon Founder and then CEO explained, “millions of people love Whole Foods Market because they offer the best natural and organic foods, and they make it fun to eat healthy.” Recently, Amazon has brought its “just walk out” checkout technology to Whole Foods, in an effort to increase ease and convenience. Will that be enough to bring customers back to Whole Foods?
To learn more about the data behind this article and what Placer has to offer, visit https://www.placer.ai/.







Sign up to receive our stories in your inbox.
Data is changing the speed of business. Investors, Corporations, and Governments are buying new, differentiated data to gain visibility make better decisions. Don't fall behind. Let us help.












Sign up to receive our stories in your inbox.
Data is changing the speed of business. Investors, Corporations, and Governments are buying new, differentiated data to gain visibility make better decisions. Don't fall behind. Let us help.





