
Source: https://secondmeasure.com/datapoints/food-delivery-services-grubhub-uber-eats-doordash-postmates/
When many Americans sheltered in their homes early in the coronavirus pandemic, meal delivery sales reached new heights. Consumer transaction data shows that in April 2020, combined sales for major meal delivery services grew 162 percent year-over-year and 59 percent compared to the previous month. Despite new macroeconomic challenges such as rising food prices, competition from dine-in restaurants, and increased fuel costs, the meal delivery industry as a whole is continuing to see some growth, though at much lower rates than those pandemic peaks. Our data reveals that in January 2023, sales for major meal delivery services grew 3 percent year-over-year, collectively.
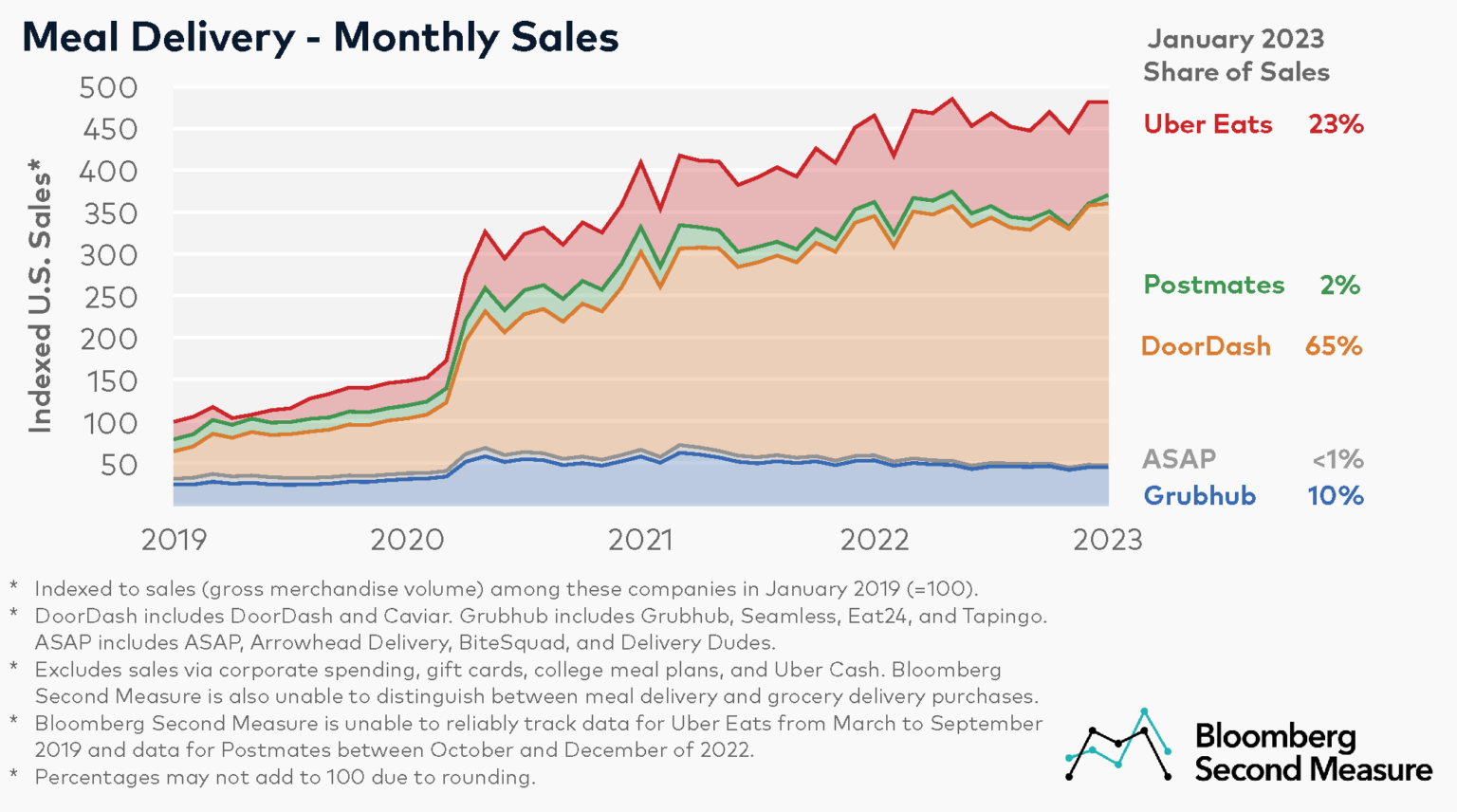
Bloomberg Second Measure’s transaction data shows that in January 2023, DoorDash (NYSE: DASH) and its subsidiary Caviar earned 65 percent of U.S. consumers’ meal delivery sales. DoorDash made its public market debut with one of the biggest IPOs of 2020, and has accounted for an increasing percentage of market share during the COVID-19 pandemic. Between January 2019 and January 2023, DoorDash’s market share among these companies roughly doubled.
Among the companies in our analysis, Uber Eats came in second place with 23 percent of sales in January 2023. It is worth noting that our sales metrics may differ from publicly reported earnings for a number of reasons. First, Bloomberg Second Measure is unable to reliably track data for Uber Eats from March to September 2019. Additionally, Bloomberg Second Measure’s data does not include Uber Eats’ purchases made using Uber Cash or purchases made by corporate customers, an area where meal delivery services are reportedly making inroads. Our analysis includes debit and credit card purchases from a panel of millions of U.S. consumers.
At the end of November 2020, Uber (NYSE: UBER) acquired Postmates in an attempt to consolidate market share and boost profitability. Postmates earned 2 percent of the U.S. meal delivery market in January 2023, bringing Uber’s total market share to 25 percent. Notably, Bloomberg Second Measure is unable to reliably track Postmates between October and December of 2022.
Grubhub and its other third-party delivery subsidiaries, which include Seamless, Eat24, and Tapingo, came in at 10 percent of U.S. meal delivery consumer spending in January 2023. (Purchases made through LevelUp, which Grubhub acquired in late 2018, are not included in our analysis. Neither are college student meal plan purchases made through Tapingo.) Grubhub was acquired by Just Eat Takeaway in June 2021.
One of the industry’s smaller services, ASAP (known as Waitr prior to its rebrand in 2022) and its subsidiaries Bite Squad, Arrowhead Delivery, and Delivery Dudes, earned less than 1 percent of national sales in January 2023. In early 2023, ASAP was delisted from the Nasdaq exchange.
Notably, data represents gross merchandise volume through these companies, not company revenue. Bloomberg Second Measure data is also unable to distinguish between meal delivery and grocery delivery sales through these companies.
Subscription meals have appeal
As meal delivery services look for new ways to grow in cities big and small, one emerging answer is subscriptions. Postmates launched Postmates Unlimited in 2016, while DoorDash and Grubhub followed suit with their own subscription options in 2018 and 2020, respectively. In November 2021, Uber also launched its new “Uber One” subscription plan, which offers benefits for both rides and delivery services.
Among subscribers who signed up for DoorDash’s DashPass in January 2022, 69 percent remained subscribed after one month. The six-month customer retention rate for DashPass subscribers in this cohort was 37 percent and the 12-month retention rate was 28 percent. In April 2022, DoorDash also launched DashPass for Students, which offers the subscription’s benefits at a reduced price.
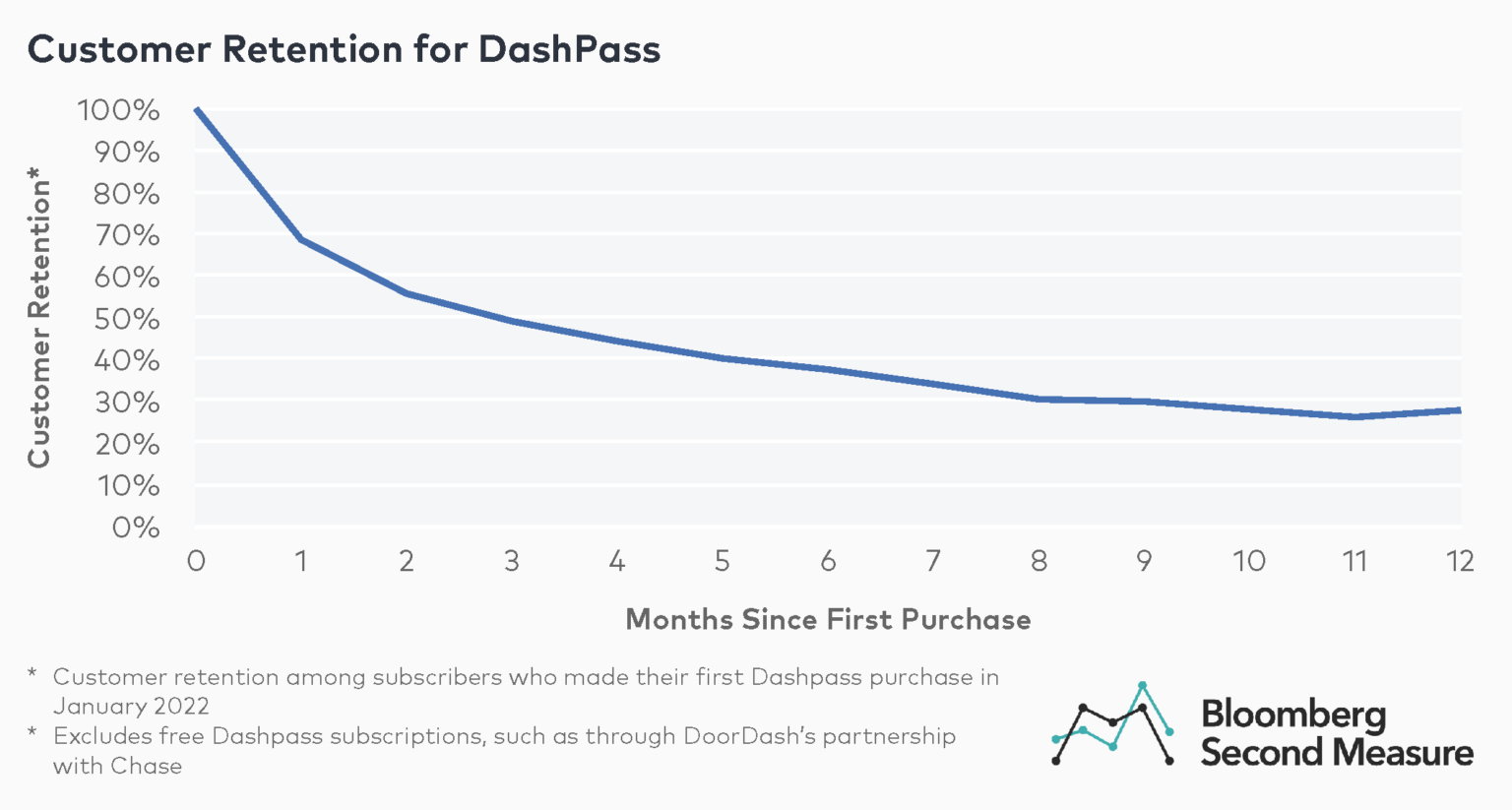
Notably, in December 2019, DoorDash also partnered with Chase to give free DashPass memberships to millions of credit card holders. These free memberships are not included in Bloomberg Second Measure’s data.
Meal delivery services vie for partnerships
Another popular growth strategy for meal delivery companies has been forming partnerships with the nation’s top chain restaurants. (Though many services have also been in the news for listing restaurants that do not want partnerships.) In 2020, DoorDash officially teamed up with Little Caesars Pizza, a brand that has never previously offered delivery. DoorDash has other deals with chains like McDonald’s and Starbucks, which both also offer delivery with Uber Eats.
Aside from restaurant partnerships, meal delivery companies are seeking ways to diversify their existing business. During the pandemic, Uber Eats launched a U.S. grocery delivery service and piloted same-day delivery with Costco. Uber has also expanded its prescription delivery partnership with Nimble and acquired alcohol delivery company Drizly. Meanwhile, DoorDash has partnerships with CVS as well as regional and national convenience stores for the delivery of household essentials. DoorDash also partnered with Albertsons to expand its grocery delivery offerings and reportedly engaged in talks to buy Instacart. In September 2021, DoorDash also announced that it was adding alcohol delivery to its app. Both Uber Eats and DoorDash have also launched nationwide shipping from select merchants. In 2022, Grubhub teamed up with Amazon to offer a free year of its Grubhub+ subscription to Amazon Prime members, and later that year partnered with rapid delivery company GoPuff for the delivery of alcohol, grocery, and essential items. ASAP, on the other hand, has sought to differentiate itself from its larger competitors through its foray into cannabis delivery and exclusive partnerships with major sports stadiums.
Rising operational costs pose challenges for meal delivery providers
As the price of food and gas continue to rise, meal delivery companies have responded to these inflationary pressures in different ways. For example, Uber Eats implemented a fuel surcharge for consumers, starting in March 2022. DoorDash launched a gas rewards program for drivers to aid with rising fuel costs, while Grubhub has boosted driver pay per mile. At the end of 2022, DoorDash also announced layoffs in an effort to improve efficiency.
Fewer customers are loyal to a single meal delivery service
Despite overall industry growth, the battle for customers is getting more intense because fewer of today’s diners are loyal to just one service. (Grubhub’s former CEO cited “promiscuous customers” as a hindrance to his company’s growth.) As more restaurants form exclusive delivery partnerships and meal delivery services offer incentives like memberships and discounts, more diners are going to have to hop between apps to cover all their favorite takeout spots and find the best deals. The least loyal customers, it seems, will also be the most well fed.
To learn more about the data behind this article and what Second Measure has to offer, visit https://secondmeasure.com/.







Sign up to receive our stories in your inbox.
Data is changing the speed of business. Investors, Corporations, and Governments are buying new, differentiated data to gain visibility make better decisions. Don't fall behind. Let us help.












Sign up to receive our stories in your inbox.
Data is changing the speed of business. Investors, Corporations, and Governments are buying new, differentiated data to gain visibility make better decisions. Don't fall behind. Let us help.





