
Today’s Non-Qualified Mortgages: Limited Documentation and High Debt-To-Income Ratio but High Credit Score and Low Loan-To-Value Ratio
Any home loan that doesn’t comply the Qualified Mortgage (QM) rules is referred to as non-QM. The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act imposed an obligation on lenders to make a good-faith effort to determine applicants have the ability to repay a mortgage, which is known as the ability-to-repay (ATR) rule. The act also mandates the QM cannot have risky loan features like negative-amortization, interest-only, balloon payments, terms beyond 30 years and no excessive points and fees. The QM must also satisfy at least one the following criteria:
A non-QM loan is not necessarily a high-risk loan; however, as the inclusion of terms such as interest-only or limited/alternative documentation can increase the risk of repayment for lenders. Non-QM loans must satisfy the ATR requirements.
The non-QM share of total mortgage counts declined during the pandemic and reached its lowest level in 2020, at 2% of the market. However, the non-QM share has almost doubled in 2022, representing about 4% of the first mortgage market. Though the non-QM loan is a small piece of today’s mortgage market, it plays a key role in meeting the credit needs for homebuyers not able to obtain financing through the GSE or government channels. Creditworthy borrowers such as self-employed borrowers, first-time homebuyers, borrowers with substantial assets but limited income, jumbo loan borrowers and investors otherwise not qualifying for the GSE and government loans, may benefit from non-QM loan options.
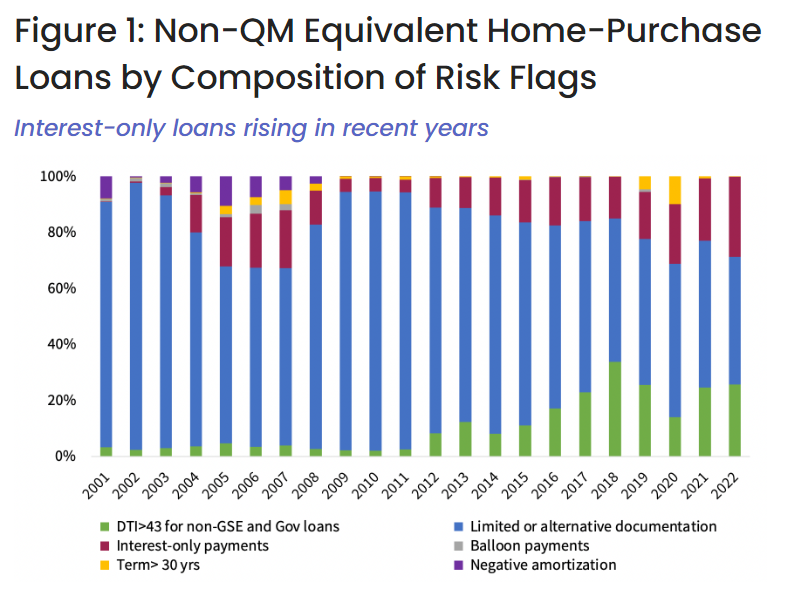
Figure 1 compares non-QM equivalent loans from 2001 to 2022 by using six major risk flags. All home-purchase loans not meeting at least one of the six QM mandated criteria are included. The three main reasons why non-QM loans originated in 2022 failed to fit in the QM box are: use of limited or alternative documentation, DTI above 43% and interest-only loans. Almost 55% of the non-QM borrowers used limited or alternative documentation, 26% exceeded 43% DTI threshold and 23% of the non-QMs were interest-only loans. Share of non-QM loans exceeding 43% DTI threshold has increased and is now 3 times higher in 2022 than in 2014 level.
Similarly, the share of interest-only loans doubled in 2022 compared with the 2014 level. Notably the risker factors such as negative amortization and balloon payments have completely vanished.
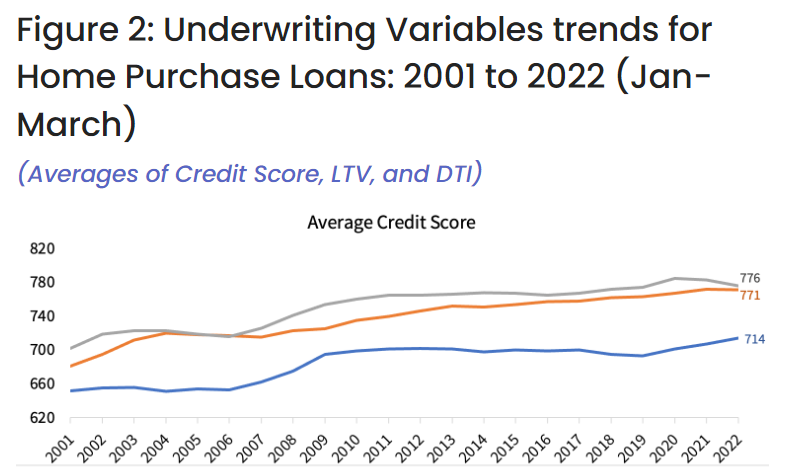
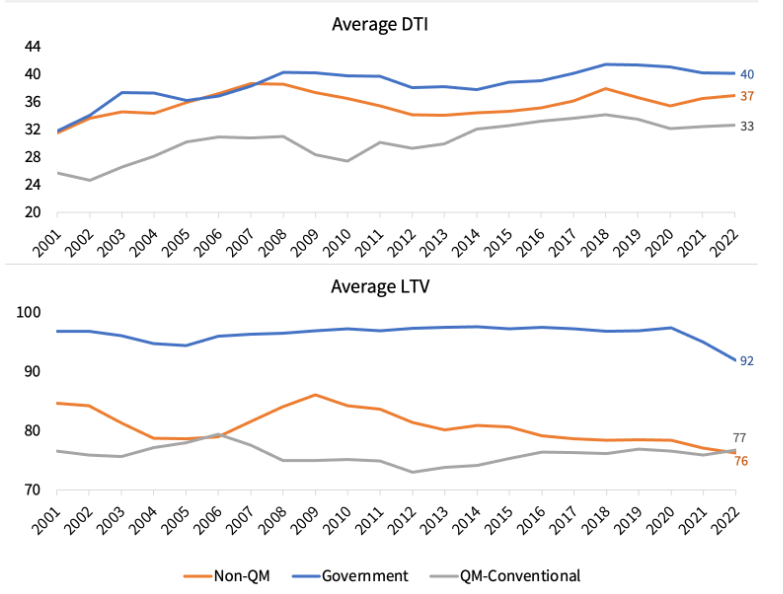
Today’s non-QMs are high-quality loans. They are vastly different and less risky than the equivalent of non-QM loans originated prior to the Great Recession. Figure 2 shows the trend of 3 major factors of underwriting for all home purchase loans: credit score, DTI and loan-to-value (LTV) ratio. The average credit score of homebuyers with non-QM in 2022 was 771 compared to 776 for homebuyers with QMs and 714 for government loans. Similarly, the average LTV for borrowers with non-QM was 76%, compared to 77% for borrowers with QMs. However, average DTI for homebuyers with non-QMs was higher compared with the DTI for borrowers with QMs.
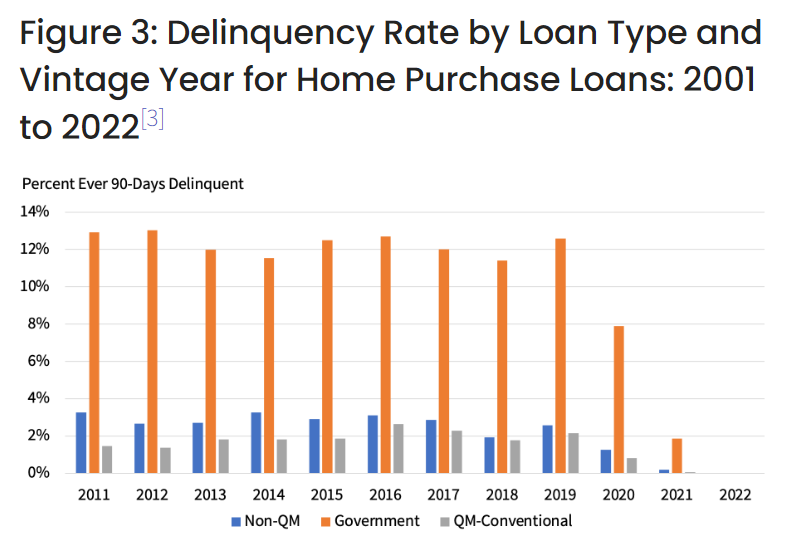
Despite the high DTI ratios, non-QMs are performing very well today. Both the non-QM and QM loans have low delinquency rates (Figure 3). In fact, the serious delinquency rate for non-QM loans is just slightly higher than the rate for QM loans and significantly lower than for the government loans.
To offset the risk of default, lenders generally set a higher interest rate on non-QM loans; for instance, the average 30-year fixed initial interest rate for non-QM was 2.9% compared to 2.6% for QM loans in 2022. Also, lenders are attracted to borrowers with higher credit score and low LTVs to help offset the added risk from a high DTI, limited documentation and interest-only on non-QM loans.
In sum, non-QM loans have helped creditworthy borrowers who cannot otherwise qualify for traditional mortgage loan programs.
To learn more about the data behind this article and what CoreLogic has to offer, visit https://www.corelogic.com/.







Sign up to receive our stories in your inbox.
Data is changing the speed of business. Investors, Corporations, and Governments are buying new, differentiated data to gain visibility make better decisions. Don't fall behind. Let us help.










Sign up to receive our stories in your inbox.
Data is changing the speed of business. Investors, Corporations, and Governments are buying new, differentiated data to gain visibility make better decisions. Don't fall behind. Let us help.





