As at-home streaming activity saw an immediate uptick during the first stay-at-home orders (mid-March 2020), new research from Comscore (Nasdaq: SCOR), a trusted partner for planning, transacting and evaluating media across platforms, shows home audio streaming usage increased sharply beginning in early April 2020 and continued to rise through mid-June 2020.
As expected, the lockdown caused a dramatic drop in vehicle miles traveled across the United Kingdom. It stagnated for about a month, then began to rise throughout May and June with the reopening of recreational sites and retail locations. Notably, weekend travel remains strong across the UK. Many cities across Europe have yet to recover to pre-COVID levels of travel, despite 10 out of the 19 countries analysed in the study reaching theirs.
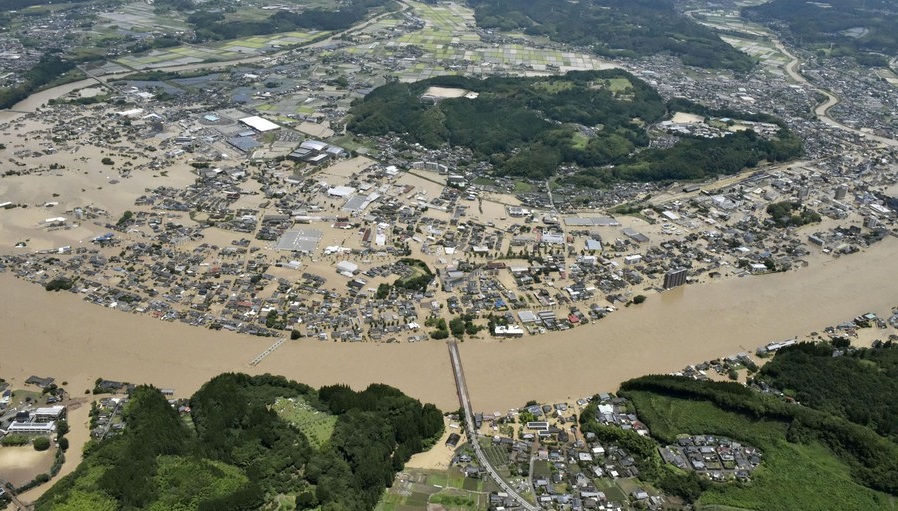
Southern Japan, like many parts of the world, has experienced extreme weather events that exceeded the capacity of dams resulting in large-scale flooding, evacuation, loss of life and costly restoration of infrastructure. The warmer atmosphere has led to extreme rainfall events that are overwhelming infrastructure that was built to specifications based on rainfall patterns of 20 to 70 years ago. The dramatic changes in weather patterns of the past decade point to the urgent need to integrate modern weather analytics into the design of future bridges, dams, roads and cities.
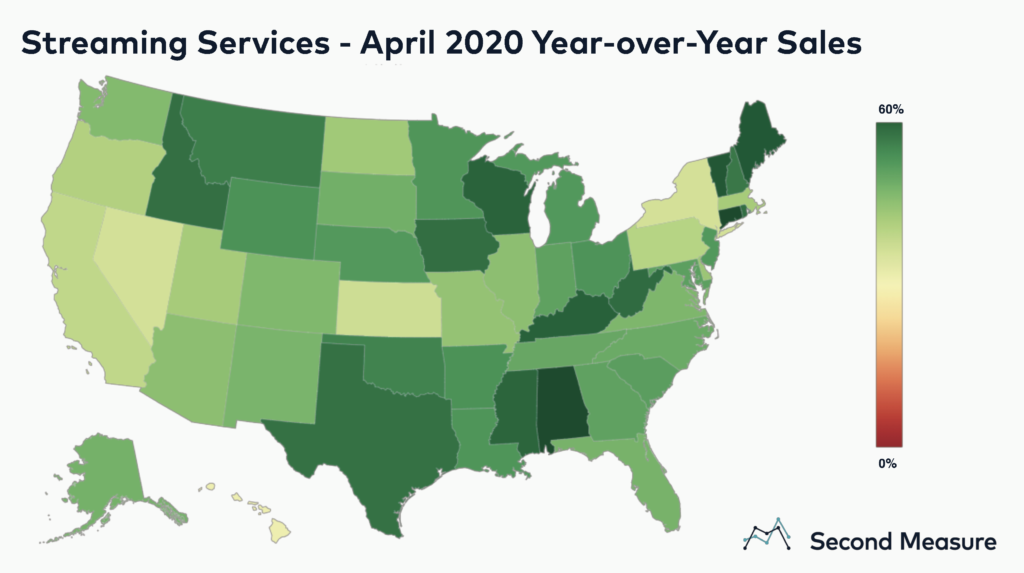
As U.S. consumers stay home amid the pandemic, they are flocking to streaming services for entertainment. The streaming industry’s sales grew 47 percent year-over-year in April 2020 compared to a 39 percent year-over-year sales increase in April 2019. Mandatory stay-at-home-orders, combined with the entry of a new market player, Disney+, and the rising popularity of socially-distant gatherings like Netflix parties, have led to the industry’s growing success.
Back in March, as people moved indoors to comply with shelter in place policies, the search for ways to stay entertained at home skyrocketed. As previous Edison Trends research on pandemic sales shows, wine subscriptions, console video games, and online marijuana sales shot up, while rideshare usage dropped. Gaming consumers have an array of choices to stay occupied at home as they head into summer, whether rain or shine in the world outside.
After months of wild spending patterns, June saw some signs of normalization with Restaurants, General Merchandise, and Grocers returning to growth profiles of low single-digits. But the virus has now resurged. The last week of June saw a material slowdown in spending growth, particularly in the lockdown-driven sectors; Ecommerce and Home categories slowed 20 points WoW, and General Merchandise and Grocers slowed 10 points to a 5% YoY decline.
With COVID cases rising again in Southern and Western states, the Washington Post reported that many hospitals are under renewed strain, with beds being filled to capacity. In order to measure the true number of hospital admissions, we have developed an algorithm that can track overnight stays for any period of time (by excluding staff and visitors).
Even after restrictions are lifted, many consumers still plan to shift their spending online. A May 2020 survey of Checkout panelists found 26% of consumers plan to shop more online at non-grocery retailers once social distancing restrictions are lifted, while only 16% plan to shop more in stores. “We’ll leapfrog three years in terms of online adoption,” said Chief Industry Advisor Marshal Cohen when asked to predict how the shift to e-commerce will play out after restrictions are lifted and a new normal sets in.
The popularity of plant-based meat has quietly established itself as a mainstay across the restaurant and grocery industry—in fact, the plant-based meat industry is projected to reach $85 billion by 2030. Increased adoption of veganism stemming from environmental and health concerns is expected to further escalate the demand for plant-based products. And in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, consumers may also be hungry for more sustainable meat options for fears over any potential meat supply chain issues amidst Covid-19.
With the COVID-19 pandemic and persistent social injustices Americans have been consuming more news. Prior to COVID-19, mobile app usage of traditional news providers was in a state of decline and only worsening. From last July through January of this year Fox News and CNN average app usage was down 18.6% and 2.5% YoY, respectively. For the same period, The New York Times averaged growth of 1.3%, however was trending significantly negative.
From a high level, downtown areas have been slow to recover. Visitation remains very low in CBGs with large volumes of office space, while the use of public areas and some parks by Residents and Locals has actually exceeded 2019 visitation levels, even though mobility overall is still down about 50% as of this writing, largely due to out-of-town Workers staying home and Tourists staying away.
As we make our way deeper into the retail recovery, the question of the lingering impact on certain behavioral changes comes to the forefront. What’s changed? How much did it change? And which of these changes have true staying power? And nowhere is this question more significant than for top QSR brands that had a clear morning orientation.
The latest data from Huq’s ‘Daily Distances’ indicator shows that New York residents continue to trail 11 major US and European centres in terms of population mobility as caution prevails. Latest figures demonstrate that the average daily distances covered by New Yorkers has yet to regain 40% of mean pre-lockdown levels, in stark contrast to other US cities (Chicago 63%, Boston 52%, Houston 65% and Atlanta 47%) and European capitals (Madrid 47%, Paris 83%, Berlin 80% and London 65%).
When will online consumer activity return to pre-pandemic levels? To answer these questions, we looked at online consumer activity in France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the UK since the start of the pandemic, and analysed how that activity has evolved over time.
When COVID initially hit there was an enormous shift in consumer behavior across the economy. Online video services like Zoom saw user counts explode from 10M to over 200M users. Similar growth was seen across online workouts, online video, ecommerce and online events. One form of online interaction that didn’t see this boost was online dating.
Using mobile app data from Apptopia we can see the number of downloads and sessions for these apps both within the United States and internationally.
Lex Machina continues to explore how courts are affected by the social changes due to the COVID-19 (coronavirus) pandemic. Our analysis of court activity through March and the first two weeks of April in 2020 compared to the previous two years revealed the following
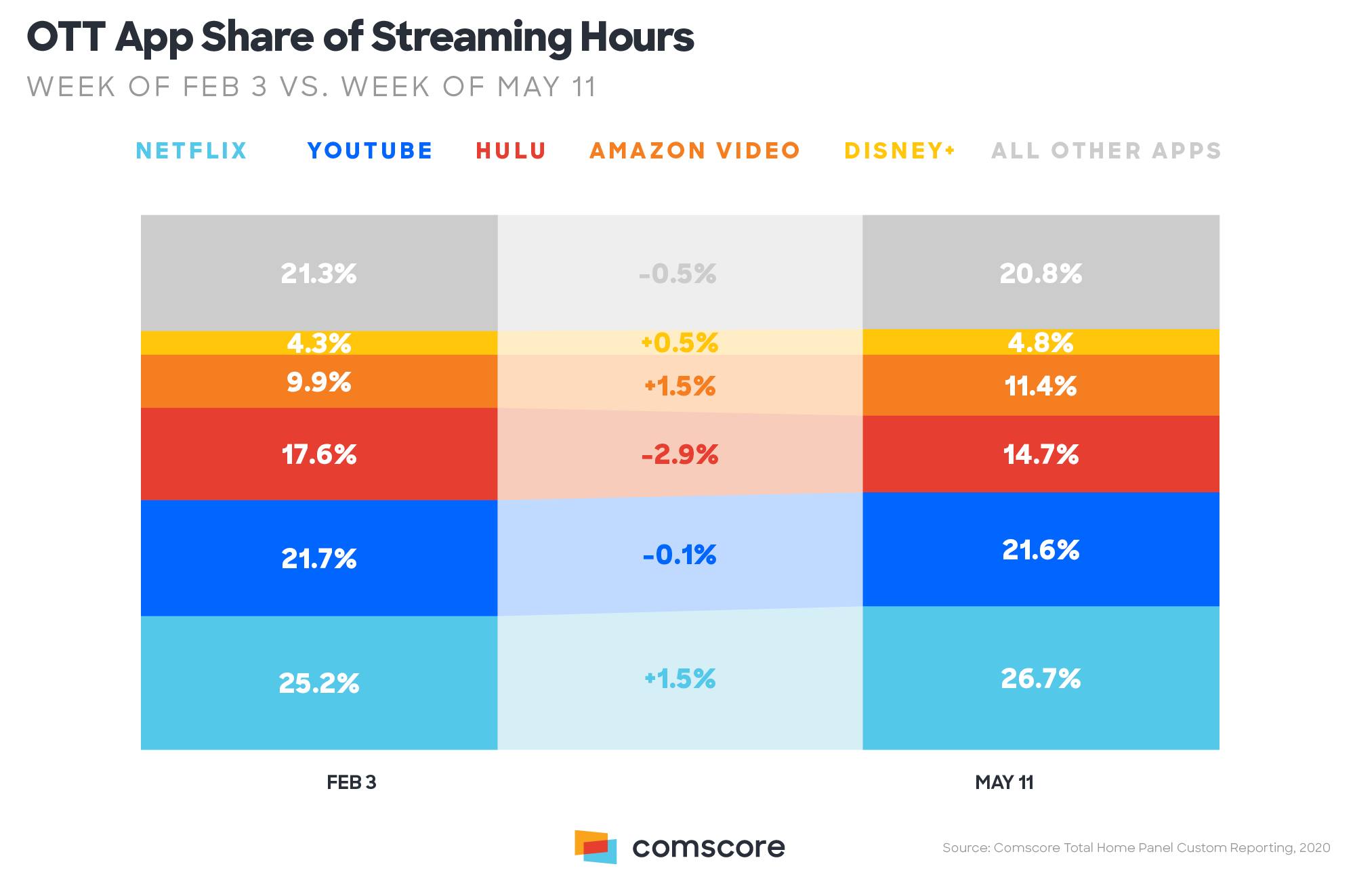
As millions of Americans adjusted to working from home and having to practice distance learning due to the COVID-19 pandemic, new research from Comscore (Nasdaq: SCOR), a trusted partner for planning, transacting and evaluating media across platforms, shows engagement with streaming services and year-over-year in-home data usage surged in the beginning of May 2020.
Life under lockdown has presented the Foodservice industry with its biggest challenge for a generation and footfall under forced closures has dropped by well over 90%. However, Huq’s Foodservice Indicator, which tracks footfall activity across Restaurants, Quick Service Restaurants (QSR) and Pubs, shows footfall to pubs has been increasing while offering some clues as to how certain businesses have adapted during this period to maintain a presence and survive.
The key to any economic recovery in the US is relaxing social distancing. Many businesses such as restaurants, gyms, doctors and hotels can’t operate profitably at 50% or lower capacity. Most restaurants run on razor thin margins, so filling seats and cramming them together is essential for their survival. In this article we examine the year to date recovery of the restaurant industry in the US.
As people around the world quarantined, the first thing people turned to in these desperate times was toilet paper. The second thing they turned to was Netflix, or Hulu or a host of other online video providers. The surge of Netflix hours had many concerned that the Internet would crash.